- What Are Common Causes of .BOOT Files Lost or Failure?
- How to recover lost .BOOT files?
- Programs to recover .BOOT files
- How to open file with .BOOT extension?
What Are Common Causes of ".BOOT" Files Lost or Failure?
There are several common causes of ".BOOT" files being lost or experiencing failure:
- Accidental deletion: Users may accidentally delete the ".BOOT" files while trying to clean up or organize their system.
- Virus or malware infection: Malicious software can corrupt or delete ".BOOT" files, leading to boot failure.
- Operating system errors: Errors during the installation, update, or upgrade of the operating system can cause ".BOOT" files to be lost or become corrupted.
- Hard drive or storage device failure: If the hard drive or storage device where the ".BOOT" files are located fails, it can result in the loss or corruption of these files.
- Power outages or improper shutdowns: Sudden power outages or improper shutdowns can interrupt the booting process and cause ".BOOT" file corruption or loss.
- Software conflicts: Conflicts between different software or incompatible software installations can lead to ".BOOT" file failure.
- Hardware issues: Faulty hardware components, such as a malfunctioning motherboard or RAM, can cause ".BOOT" file issues.
- Human error: Mistakes made during system configuration, such as modifying critical boot files, can result in ".BOOT" file failure.
It is important to regularly backup important system files, including ".BOOT" files, to minimize the impact of such failures.
How to recover lost ".BOOT" files?
Sometimes while working with a computer, laptop or other stationary or mobile devices, you may encounter various bugs, freezes, hardware or software failures, even in spite of regular updates and junk cleaning. As a result, an important ".BOOT" file may be deleted.

🧺 How to Recover Files and Folders After Sending Them to the Recycle Bin and Deleting? (Windows 11)
By no means should you think that the only way to recover a ".BOOT" file is always to create it once more.
Use programs for recovering ".BOOT" files if a file was lost after accidental or deliberate deleting, formatting the memory card or the internal storage, cleaning the storage device, after a virus attack or a system failure.
Programs to recover ".BOOT" files
Looking for a way to get files back? In cases when files were deleted and they cannot be restored by using standard operating system tools, use Hetman Partition Recovery.
Follow the directions below:
-
Download Hetman Partition Recovery, install and start the program.
-
The program will automatically scan the computer and display all hard disks and removable drives connected to it, as well as physical and local disks.
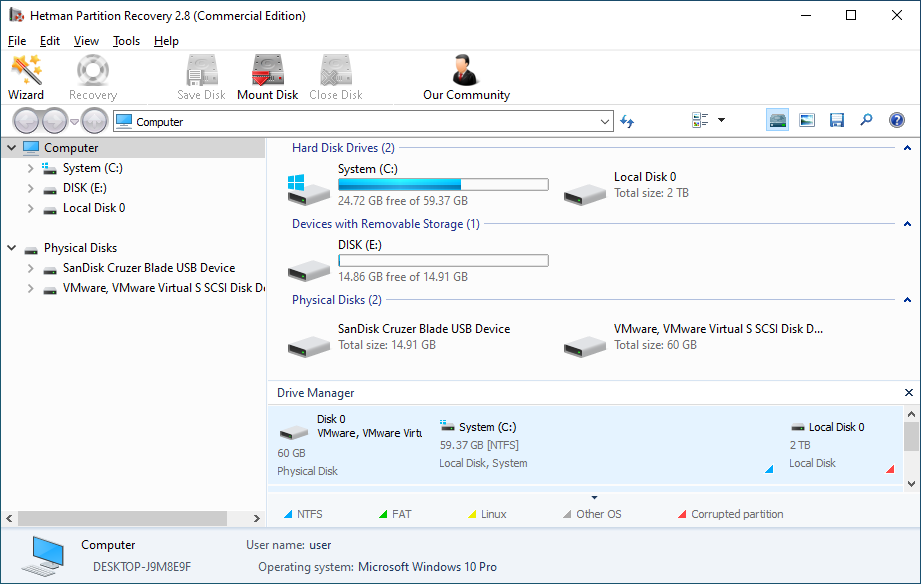
-
Double-click on the disk from which you need to recover ".BOOT" files, and select analysis type.
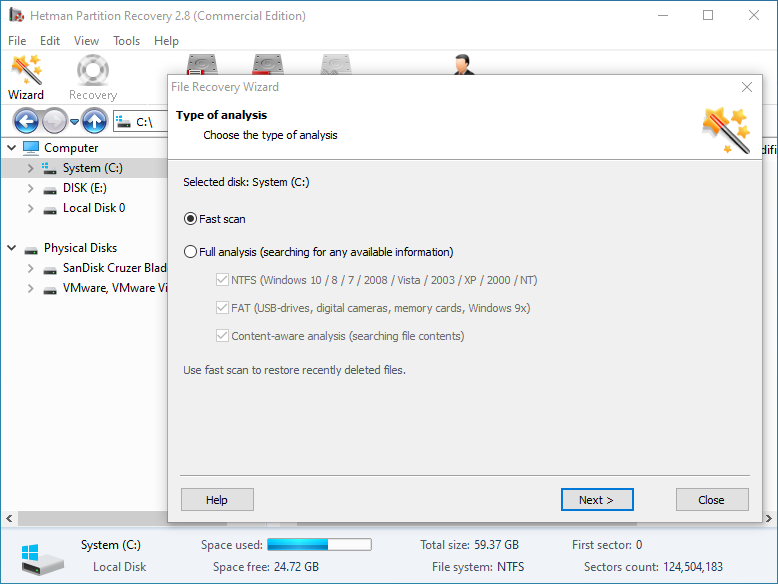
-
When the scanning is over, you will be shown the files for recovery.
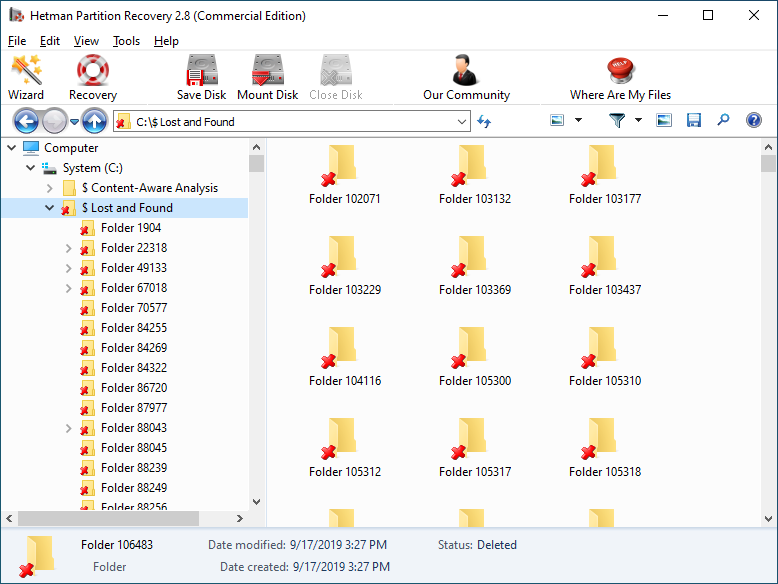
-
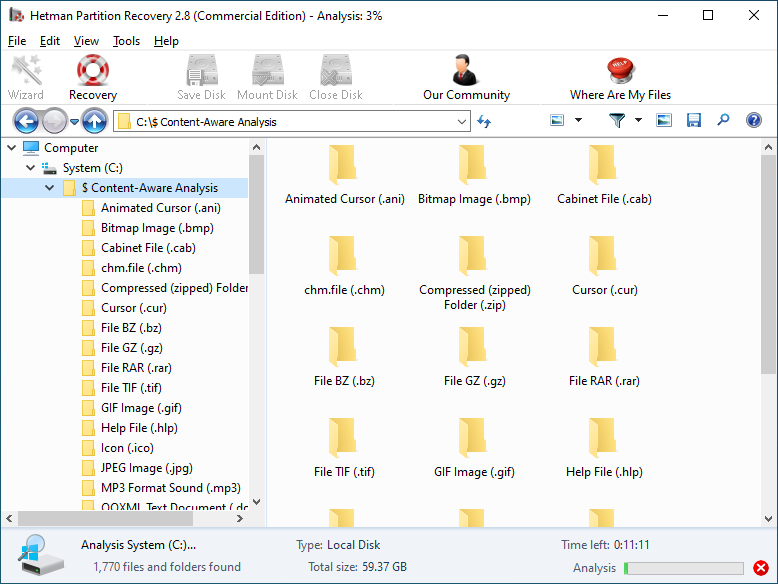
To find a file you need, use the program’s interface to open the folder it was deleted from, or go to the folder "Content-Aware Analysis" and select the required file type.
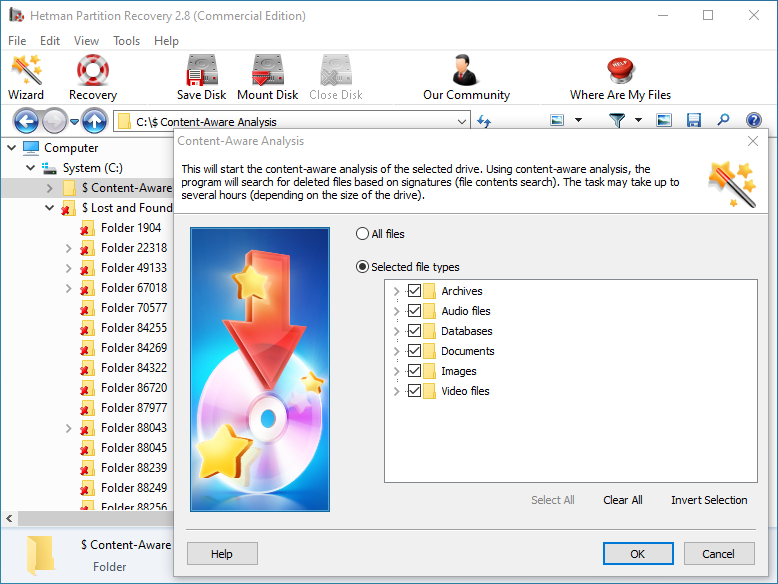
-
Select the files you have been looking for and click "Recovery".
-
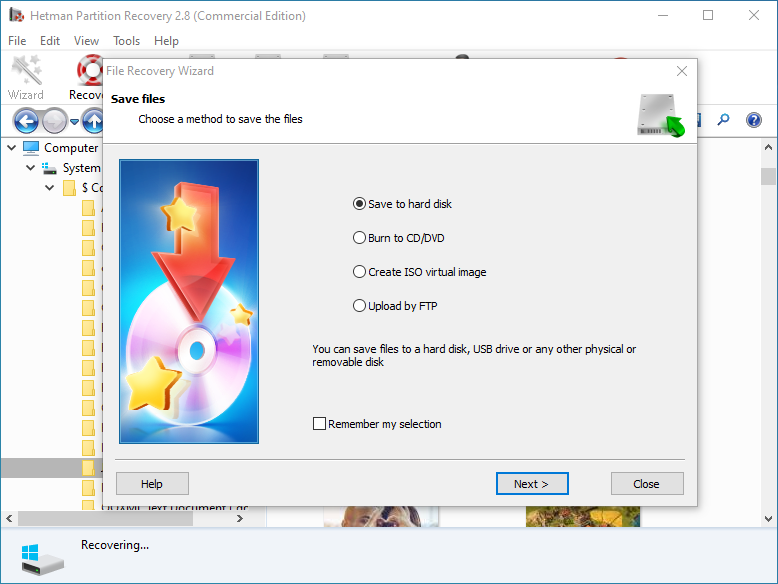
Choose one of the methods for saving the files and recover them.
How to open file with ".BOOT" extension?
Looking for how to open a stereo installShield Boot File image file file?
Programs that open ".BOOT" files
| Windows |
|---|
|
|
Additional Information
-
File type: InstallShield Boot File
-
File extension: .BOOT
-
Developer: Flexera Software
-
Category: Settings Files
-
Format: Text



