
- Why Regular Data Recovery Tools Can’t Restore Files from RAID
- Key Information About the NAS Synology Diskstation DS118
- How to Remove Hard Disks from Your NAS and Connect Them to a PC
Why Regular Data Recovery Tools Can’t Restore Files from RAID
Conventional hard drives store user data by writing it sequentially across the disk surface, which means an entire file is typically located on a single drive. In contrast, when data is written to a RAID array, each file is split into multiple fragments. These fragments are then distributed and written in sequence across all the drives in the array. Depending on the configuration, fragment sizes can range from 2 KB to 2 MB, so every file is physically stored across several disks at once.
This approach significantly increases read and write performance — after all, writing two halves of a 1 GB file to two drives simultaneously is much faster than writing the full 1 GB to a single disk. However, this same mechanism makes file recovery far more complex.
Different RAID levels use different methods to distribute and protect data. On top of that, manufacturers like Synology often add their own proprietary structures and variations. As a result, data can be written to disks in many different formats, and each requires a specific approach during recovery.
What are the risks of data loss due to firmware or software malfunctions in NAS Synology Diskstation DS118 devices?
There are several risks of data loss due to firmware or software malfunctions in NAS Synology Diskstation DS118 devices:
- Corrupted Data: Firmware or software malfunctions can lead to data corruption, rendering the files and folders stored on the NAS inaccessible or unreadable.
- System Instability: Malfunctions in the firmware or software can cause the NAS device to become unstable, leading to unexpected crashes or freezes. This instability can result in data loss if files are being written or accessed during such events.
- Disk Failure: Firmware or software issues can potentially cause disk failures or errors, resulting in data loss. If the NAS fails to properly manage or communicate with the disks, it can lead to data corruption or complete loss of data stored on the affected disk.
- Incompatibility: Incompatibilities between the NAS firmware or software and other components, such as hard drives or network equipment, can cause data loss. For example, a firmware update might introduce compatibility issues that result in data becoming inaccessible or lost.
- Data Migration Errors: Firmware or software malfunctions during data migration processes, such as upgrading to a new NAS model or restoring from a backup, can lead to data loss. Errors or interruptions during these processes can corrupt data or result in incomplete transfers.
- User Error Amplification: Firmware or software malfunctions can amplify the impact of user errors. For instance, if a user accidentally deletes a file, a malfunctioning firmware or software might fail to properly handle the deletion, resulting in permanent data loss.
To mitigate these risks, it is essential to regularly update the firmware and software of the NAS device, maintain proper backups, and ensure the integrity and compatibility of the hardware components used with the NAS. Additionally, following best practices for data management, such as avoiding abrupt power cuts or improper shutdowns, can help minimize the chances of data loss due to firmware or software malfunctions.
How to Remove Hard Disks from Your NAS and Connect Them to a PC
Although the NAS Diskstation DS118 can be accessed over the network, you still need to remove its hard disks and connect them directly to a Windows PC. Only then can the recovery software properly scan and analyze the drives. Follow these steps:
-
Power off the NAS and disconnect it from the power source.
WARNING! Before removing any drives, carefully read the device manual. Improper actions may damage both the NAS enclosure and the hard disks in the RAID array.
-
Remove the hard disks one by one, gently sliding each drive out of its slot. Remember that hard disks are highly sensitive: any impact or drop can cause serious physical damage.
-
Label each hard disk according to its position inside the NAS. The order of the drives is crucial for correct RAID reconstruction.
-
Connect the drives to your computer. In this video, we explain which ports you can use to connect hard disks and what to do if your PC does not have enough free connectors.
Go to view
Step-by-Step Data Recovery with Hetman RAID Recovery
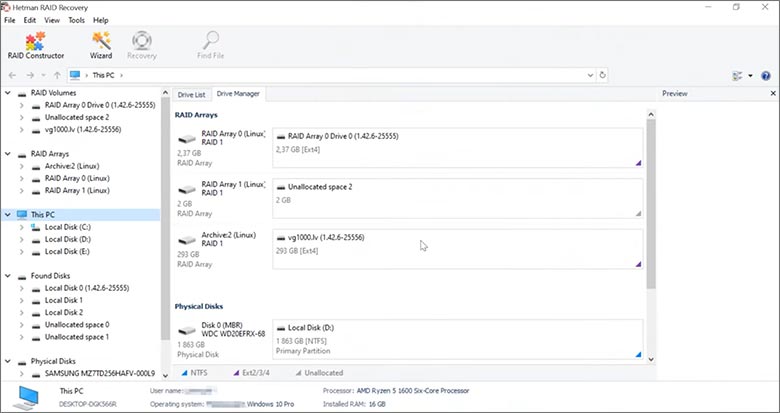
This program restores data from damaged RAID arrays and is fully compatible with Synology Diskstation DS118. Each hard disk in the array contains technical metadata describing how files were written. When launched, Hetman RAID Recovery analyzes this metadata, automatically reconstructs the damaged array, and provides access to its contents. After that, you can browse the recovered disk and save your files. The program can also restore files that were accidentally deleted from the network drive.

How to recover data from a Synology
Diskstation DS118 has 1 HDD slots, and it supports the following array types:
- Basic;
NAS supports:
- EXT4;
- EXT3 (External Disk Only);
- FAT (External Disk Only);
- exFAT (External Disk Only);
- NTFS (External Disk Only);
- HFS+ (External Disk Only);
How to Safely Recover Data from Disk Images
This utility allows you to create a complete copy of a disk and work with the disk image instead of the physical drive. This approach helps protect your data from:
- Overwriting during the recovery process;
- Additional data loss caused by bad sectors;
- User errors.
To create a disk image, follow these steps:
-
Ensure you have enough free space to store the image. Its size will typically match the size of the original disk.
-
In the main window, select the target disk and choose Tools - Save Disk. You can also select multiple disks if needed.
-
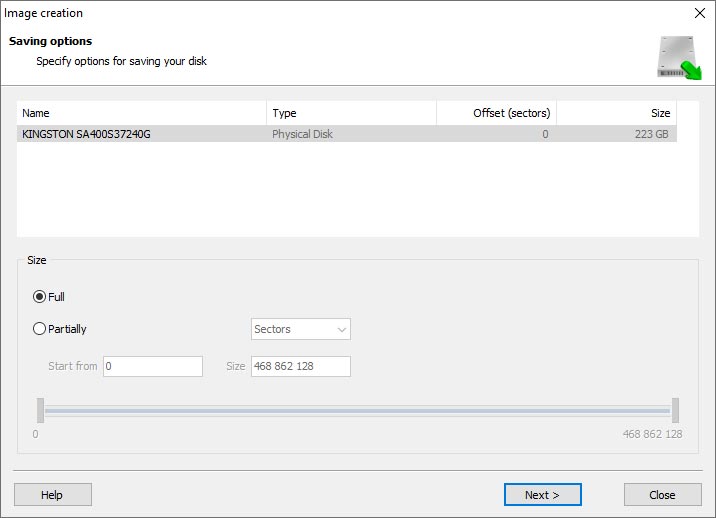
When the Image Creation Wizard opens, select whether you want to save the entire disk or only a specific region. Adjust the settings and click Next.
-
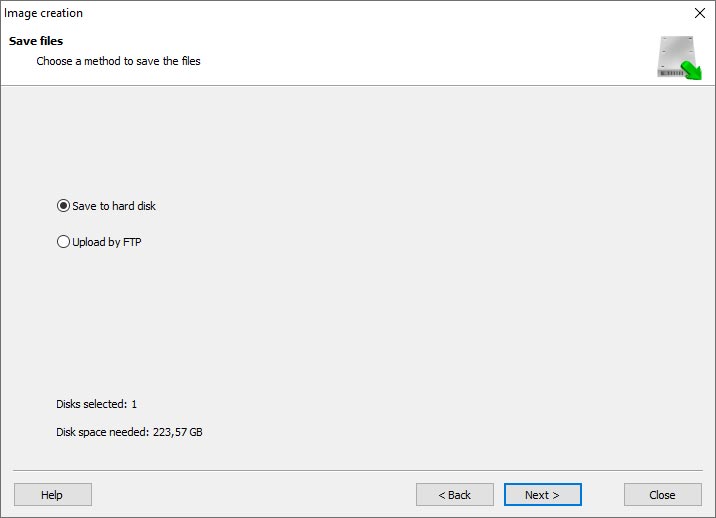
Choose the directory where the image will be saved. You may select any available disk connected to your PC or upload the image via FTP.
Where Are the User’s Files Actually Stored?
The Synology Diskstation DS118 network-attached storage keeps DSM (DiskStation Manager) operating system files on a separate RAID 1 (mirrored) array. Usually, all NAS systems create several volumes on every hard disk, and the first of them takes up to 2 Gb of space. This is where operating system files are stored. Other volumes are united into a RAID array where user’s data is written.
RAID Recovery Software: Detailed Comparison
| Product | Operating system | RAID controller support | Supported file systems | Virtual RAID controller support | Data recovery from damaged RAID | File preview |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hetman RAID Recovery | Windows, Linux, MacOS | Yes, over 100 controllers | FAT, exFAT, NTFS, ReFS, APFS, HFS+, Ext4, Ext3, Ext2, ReiserFS, Btrfs, VMFS, Hikvision, XFS, UFS, ZFS | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| DiskInternals RAID Recovery | Windows | Yes, over 10 controllers | FAT, NTFS, Ext2/3/4, HFS+ | No | Yes | Yes |
| R-Studio | Windows, Mac, Linux | Yes, over 20 controllers | FAT, NTFS, Ext2/3/4, HFS+ | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| UFS Explorer RAID Recovery | Windows, Mac, Linux | Yes, over 100 controllers | FAT, NTFS, Ext2/3/4, HFS+ | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| EaseUS Data Recovery | Windows | Yes, over 20 controllers | FAT, NTFS, Ext2/3/4, HFS+ | No | Yes | Yes |
| ReclaiMe Free RAID Recovery | Windows | Yes, over 100 controllers | FAT, NTFS, Ext2/3/4, HFS+ | Yes | Yes | Yes |



