
- Why Regular Data Recovery Tools Can’t Restore Files from RAID
- Key Information About the NAS Digiever DS-16332-RM Pro+
- How to Remove Hard Disks from Your NAS and Connect Them to a PC
Why Regular Data Recovery Tools Can’t Restore Files from RAID
Conventional hard drives store user data by writing it sequentially across the disk surface, which means an entire file is typically located on a single drive. In contrast, when data is written to a RAID array, each file is split into multiple fragments. These fragments are then distributed and written in sequence across all the drives in the array. Depending on the configuration, fragment sizes can range from 2 KB to 2 MB, so every file is physically stored across several disks at once.
This approach significantly increases read and write performance — after all, writing two halves of a 1 GB file to two drives simultaneously is much faster than writing the full 1 GB to a single disk. However, this same mechanism makes file recovery far more complex.
Different RAID levels use different methods to distribute and protect data. On top of that, manufacturers like Digiever often add their own proprietary structures and variations. As a result, data can be written to disks in many different formats, and each requires a specific approach during recovery.
Can the use of specific data compression or deduplication techniques impact the performance and data integrity on NAS Digiever DS-16332-RM Pro+ devices?
The impact of specific data compression or deduplication techniques on the performance and data integrity of NAS Digiever DS-16332-RM Pro+ devices can vary depending on various factors.
Data compression techniques aim to reduce the size of data by encoding it in a more efficient way. This can result in reduced storage requirements and improved transfer speeds. However, the compression and decompression processes can introduce some overhead, which may slightly impact the performance of the device. The impact on data integrity is generally minimal, as long as the compression algorithm used is reliable and does not introduce any errors during compression or decompression.
Deduplication techniques, on the other hand, eliminate duplicate copies of data, thereby reducing storage space. This can also lead to improved performance as it reduces the amount of data that needs to be processed and transferred. Deduplication techniques typically rely on algorithms that identify and eliminate duplicate data blocks, ensuring that only one copy is stored. As long as the deduplication algorithm is well-implemented and the data integrity checks are in place, the impact on data integrity should be minimal.
It is important to note that the specific implementation and configuration of these techniques can vary across different NAS devices, including the Digiever DS-16332-RM Pro+. Therefore, it is recommended to consult the manufacturer's documentation or support resources to understand the exact impact of data compression or deduplication techniques on performance and data integrity for this particular device.
How to Remove Hard Disks from Your NAS and Connect Them to a PC
Although the NAS DS-16332-RM Pro+ can be accessed over the network, you still need to remove its hard disks and connect them directly to a Windows PC. Only then can the recovery software properly scan and analyze the drives. Follow these steps:
-
Power off the NAS and disconnect it from the power source.
WARNING! Before removing any drives, carefully read the device manual. Improper actions may damage both the NAS enclosure and the hard disks in the RAID array.
-
Remove the hard disks one by one, gently sliding each drive out of its slot. Remember that hard disks are highly sensitive: any impact or drop can cause serious physical damage.
-
Label each hard disk according to its position inside the NAS. The order of the drives is crucial for correct RAID reconstruction.
-
Connect the drives to your computer. In this video, we explain which ports you can use to connect hard disks and what to do if your PC does not have enough free connectors.
Go to view
Step-by-Step Data Recovery with Hetman RAID Recovery
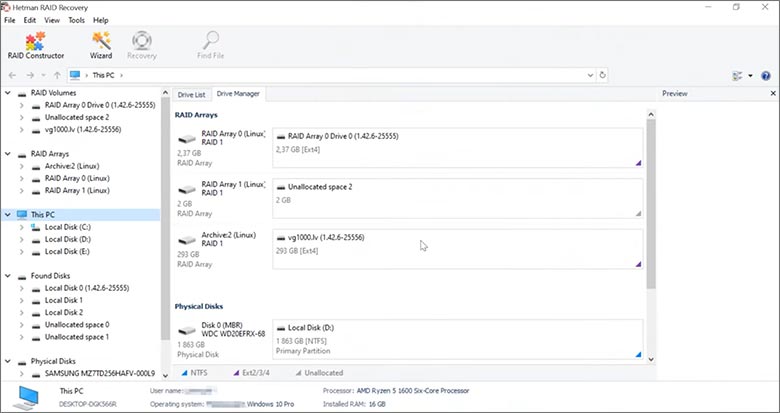
This program restores data from damaged RAID arrays and is fully compatible with Digiever DS-16332-RM Pro+. Each hard disk in the array contains technical metadata describing how files were written. When launched, Hetman RAID Recovery analyzes this metadata, automatically reconstructs the damaged array, and provides access to its contents. After that, you can browse the recovered disk and save your files. The program can also restore files that were accidentally deleted from the network drive.

How to recover data from a Digiever
DS-16332-RM Pro+ has 16 HDD slots, and it supports the following array types:
- RAID 0;
- RAID 1;
- RAID 5;
- RAID 6;
- RAID 50;
- RAID 60;
- JBOD;
NAS supports:
- exFAT, VFAT, FAT 12 / 16 / 32;
- NTFS / ReFS;
- APFS / HFS+;
- Ext2 / 3 / 4 / ReiserFS / XFS / UFS / ZFS / Btrfs;
- VMFS / HikvisionFS;
How to Safely Recover Data from Disk Images
This utility allows you to create a complete copy of a disk and work with the disk image instead of the physical drive. This approach helps protect your data from:
- Overwriting during the recovery process;
- Additional data loss caused by bad sectors;
- User errors.
To create a disk image, follow these steps:
-
Ensure you have enough free space to store the image. Its size will typically match the size of the original disk.
-
In the main window, select the target disk and choose Tools - Save Disk. You can also select multiple disks if needed.
-
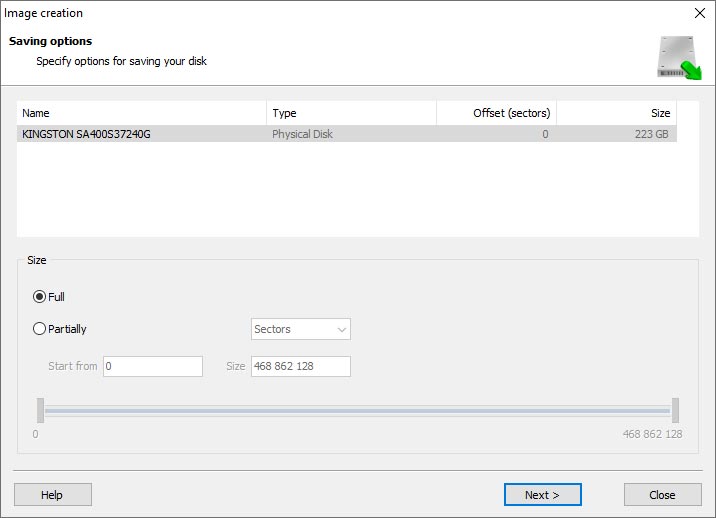
When the Image Creation Wizard opens, select whether you want to save the entire disk or only a specific region. Adjust the settings and click Next.
-
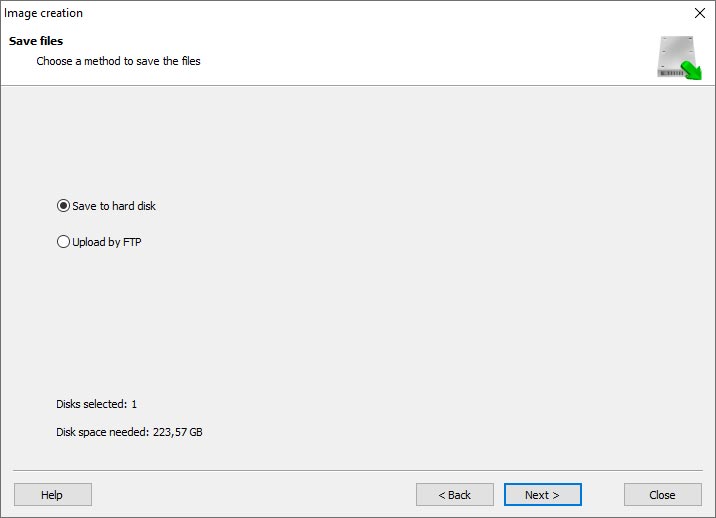
Choose the directory where the image will be saved. You may select any available disk connected to your PC or upload the image via FTP.
Where Are the User’s Files Actually Stored?
The Digiever DS-16332-RM Pro+ network-attached storage keeps OS Linux operating system files on a separate RAID 1 (mirrored) array. Usually, all NAS systems create several volumes on every hard disk, and the first of them takes up to 2 Gb of space. This is where operating system files are stored. Other volumes are united into a RAID array where user’s data is written.
RAID Recovery Software: Detailed Comparison
| Product | Operating system | RAID controller support | Supported file systems | Virtual RAID controller support | Data recovery from damaged RAID | File preview |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hetman RAID Recovery | Windows, Linux, MacOS | Yes, over 100 controllers | FAT, exFAT, NTFS, ReFS, APFS, HFS+, Ext4, Ext3, Ext2, ReiserFS, Btrfs, VMFS, Hikvision, XFS, UFS, ZFS | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| DiskInternals RAID Recovery | Windows | Yes, over 10 controllers | FAT, NTFS, Ext2/3/4, HFS+ | No | Yes | Yes |
| R-Studio | Windows, Mac, Linux | Yes, over 20 controllers | FAT, NTFS, Ext2/3/4, HFS+ | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| UFS Explorer RAID Recovery | Windows, Mac, Linux | Yes, over 100 controllers | FAT, NTFS, Ext2/3/4, HFS+ | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| EaseUS Data Recovery | Windows | Yes, over 20 controllers | FAT, NTFS, Ext2/3/4, HFS+ | No | Yes | Yes |
| ReclaiMe Free RAID Recovery | Windows | Yes, over 100 controllers | FAT, NTFS, Ext2/3/4, HFS+ | Yes | Yes | Yes |




Recovering data from a NAS device that has been affected by firmware corruption or update failure can be challenging. However, it is possible to recover data in some cases. Here are a few steps you can try:
a. Remove the hard drives: Carefully remove the hard drives from the NAS device.
b. Connect the drives to a computer: Use a SATA-to-USB adapter or a compatible NAS enclosure to connect the drives to a computer.
c. Use data recovery software: Use data recovery software like Recuva, EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard, or similar tools to scan the drives and attempt to recover the data.
d. Seek professional help if necessary: If the DIY attempts fail, consider reaching out to professional data recovery services.
Remember, data recovery success depends on various factors, including the extent of firmware corruption, the state of the drives, and the availability of backups. It is always recommended to regularly backup important data to avoid such situations.